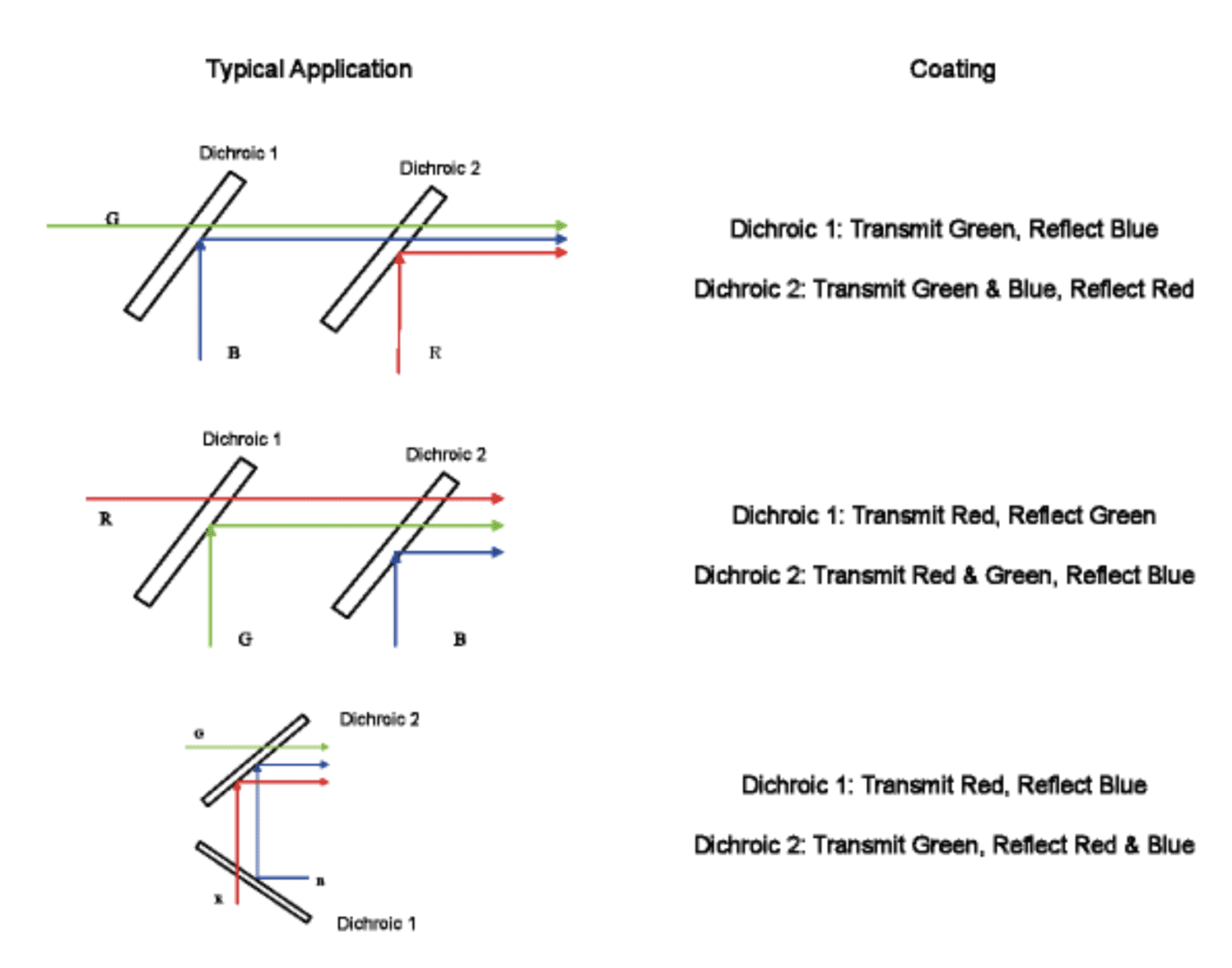
A dichroic mirror is specifically designed to reflect certain wavelengths of light while transmitting others. Its main purpose is to split or combine different light wavelengths.
For instance, in fluorescence microscopy, a dichroic mirror reflects excitation light (e.g., blue light) toward the sample while transmitting longer-wavelength emitted light (e.g., green light) to the detector.
Typically placed at a 45-degree angle to the light source, it acts as a beam-splitter, directing certain wavelengths while passing others straight through.
Typical Specifications:
Material: Borofloat or equivalent
Thickness: 0.3mm – 1.1mm