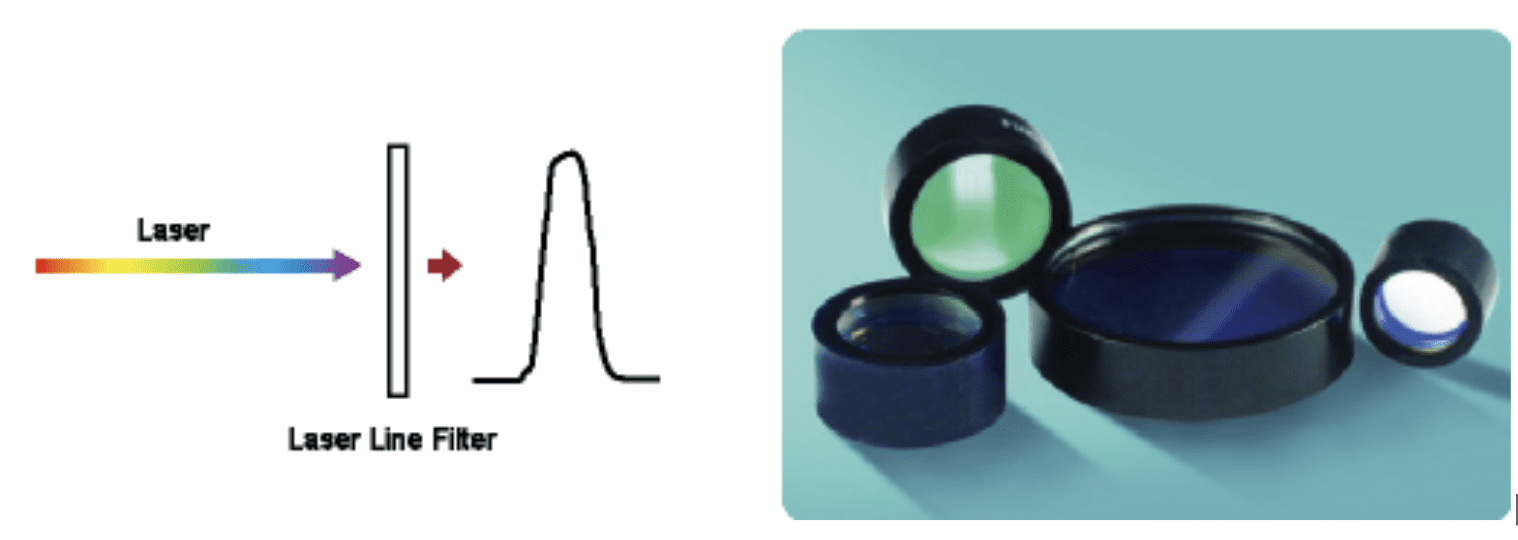
What Are Laser Line Filters?
Laser line filters are optical filters specifically designed to selectively transmit a narrow range of wavelengths (the laser line) while blocking or attenuating other wavelengths. They are commonly used in applications involving lasers, where it's essential to isolate a particular wavelength or narrow band of wavelengths to enhance measurement accuracy or reduce background noise.
Key Characteristics
Narrow Bandwidth: Laser line filters have a very narrow bandwidth, often in the range of a few nanometers, which allows them to transmit only the specific wavelength of the laser light while blocking other wavelengths.
High Transmission: These filters provide high transmission efficiency at the laser wavelength, ensuring that most of the laser light passes through the filter with minimal loss.
Deep Blocking: They offer deep blocking of unwanted wavelengths, reducing the amount of stray light and interference from other sources. This is especially important in sensitive applications like fluorescence microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and laser-based imaging systems.
Center Wavelength (CWL): The center wavelength of a laser line filter is designed to match the specific wavelength of the laser being used, such as 532 nm, 635 nm, or 1064 nm, depending on the laser type.
Applications: Laser line filters are widely used in scientific research, industrial processes, medical diagnostics, and imaging technologies where lasers are used as a light source. Examples include confocal microscopy, DNA sequencing, and flow cytometry.
These filters are critical components for improving the signal-to-noise ratio in systems that rely on precise wavelength control, helping to achieve accurate measurements and clear images.
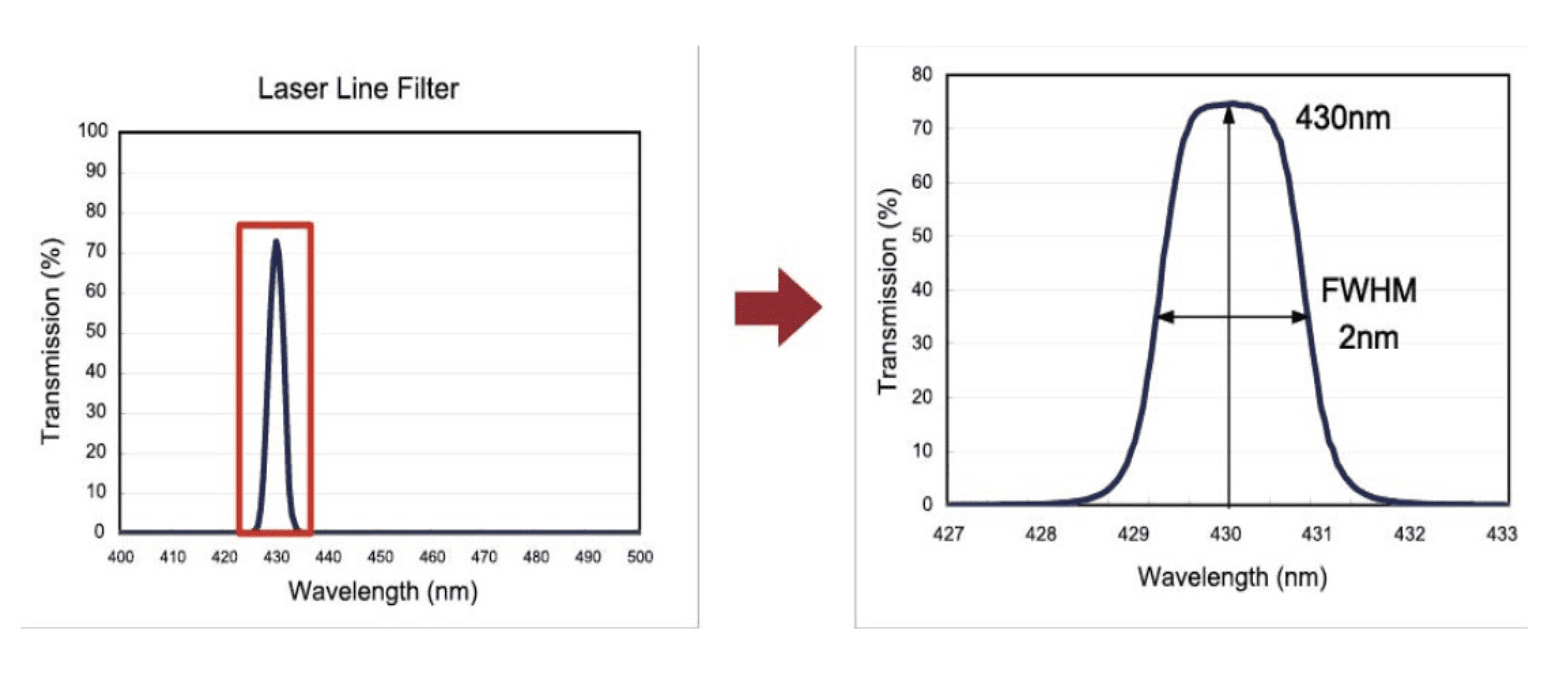

Key Features
- High peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR)
- Deep blocking
- Steep slope
- High damage threshold
- Excellent environmental stability
