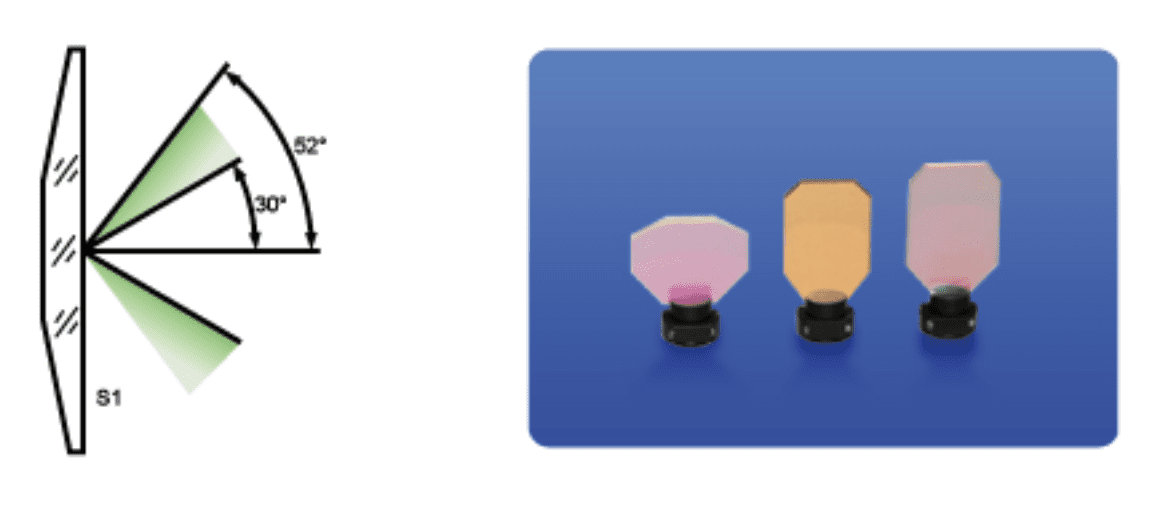

What are scanning mirrors?
Scanning mirrors are optical components used to direct and control the path of a laser beam in a precise and programmable manner. They play a crucial role in various laser scanning systems, where they rapidly move or oscillate to steer the laser beam to specific positions or patterns. Scanning mirrors are typically mounted on motors or galvanometers that provide fast and accurate movement.
Applications of Scanning Mirrors:
- Laser Projectors: Scanning mirrors are used to direct the laser beam in a precise manner to create images or patterns on surfaces, commonly found in laser light shows and laser projectors.
- Medical Devices: They are used in medical imaging systems, laser surgery equipment, and ophthalmic devices for high-speed and precise targeting.
- LIDAR Systems: Scanning mirrors are essential components in LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology for mapping and distance measurement in autonomous vehicles and other applications.
- 3D Printing: In some laser-based 3D printers, scanning mirrors are used to direct the laser beam to selectively cure or solidify material in a layer-by-layer manufacturing process.
- Bar Code Readers: Scanning mirrors help in reading barcodes by directing the laser beam across the code's surface.
Scanning mirrors are integral to systems that require fast and accurate laser beam control, enabling precise operations in various industrial, medical, and scientific applications.
Key Characteristics of Scanning Mirrors
- High-Speed Movement: Scanning mirrors are designed to move at very high speeds, allowing them to sweep the laser beam across a target area quickly and efficiently. The speed and precision of the movement are crucial for applications that require rapid scanning.
- Angle Control: These mirrors can tilt or rotate at different angles, changing the direction of the reflected laser beam with a high degree of control. The angle of movement determines the area that the laser beam covers.
- Galvanometer Mounts: Many scanning mirrors are mounted on galvanometers, which are devices that convert electrical signals into mechanical motion. Galvanometers enable precise angular positioning and fast response times, making them ideal for laser scanning applications.
- Reflective Coatings: The mirrors often have specialized coatings that optimize reflectivity for specific laser wavelengths, minimizing losses and ensuring efficient beam steering.
- Low Inertia: Scanning mirrors are typically lightweight and have low inertia, which helps them achieve faster acceleration and deceleration, improving scanning speed and accuracy.
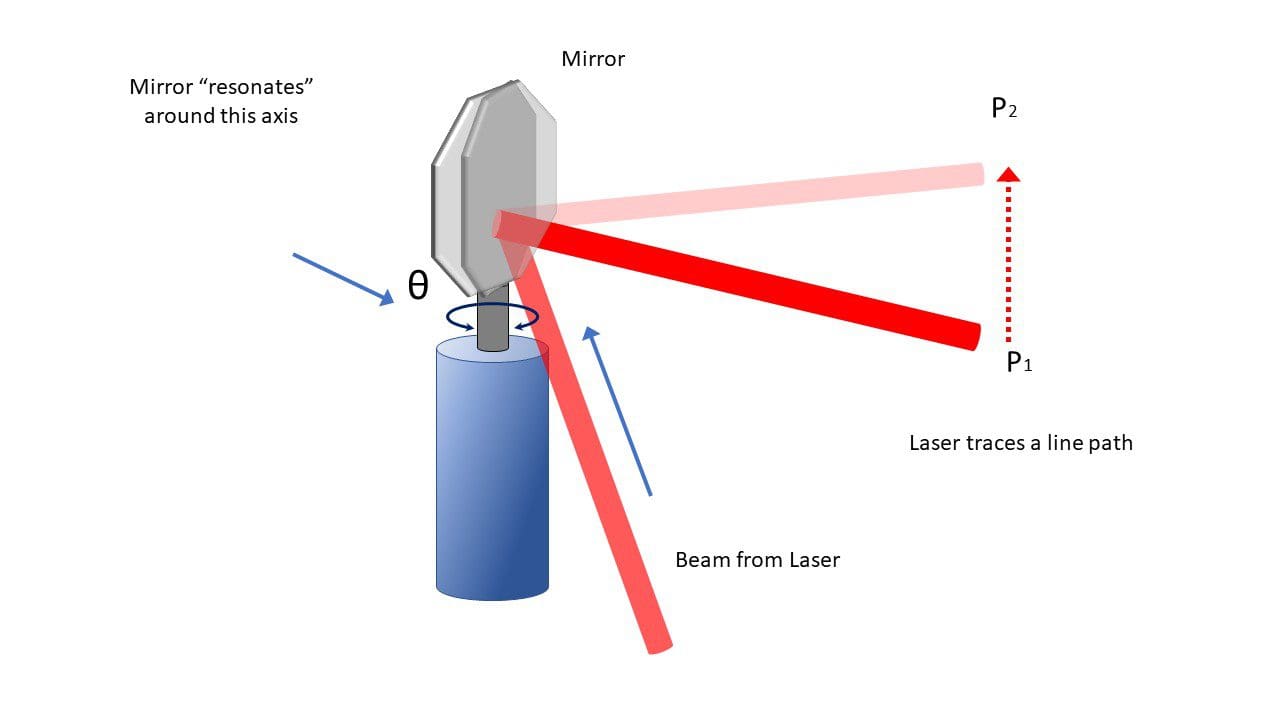

Types of Scanning Mirrors
- Single-Axis Mirrors: These mirrors move in one direction, either horizontally or vertically, to scan a laser beam.
- Dual-Axis Mirrors: These mirrors can move in both horizontal and vertical directions, allowing for more complex and flexible laser beam control.
- Polygon Mirrors: Rotating polygon mirrors have multiple reflective facets that can reflect the laser beam in different directions as they spin, often used in high-speed applications.
Typical Specifications
| Material | BK7 or Fused Silica |
| Surface Quality | 40/20 |
| Surface Flatness | λ/[email protected] |
| AOI (angle of incidence) | 45°±11° |
| Bevel | 0.3mm x 45° |
| Coating | Hard Coating |
